Over a year ago, I shared ten ways IT can help us tackle biodiversity challenges. Since then, significant progress has been made in each area. Today, I want to highlight some of the exciting startups and initiatives positively impacting biodiversity conservation through innovative technology.
https://www.linkedin.com/posts/matkoehler_biodiversity-it-wipro-activity-7056861963452076032-YLsH?utm_source=share&utm_medium=member_desktop
The Next Big Wave of Environmental Challenges
Biodiversity, the variety of life on Earth, is increasingly recognized as the next major environmental challenge. It could potentially pose an even more significant threat than climate change. While climate change has dominated the environmental agenda for decades, the degradation of biodiversity is an urgent and complex issue that demands immediate attention and action.
Biodiversity underpins the health of ecosystems. Each species, no matter how small, plays a role in maintaining ecological balance. The loss of biodiversity can lead to the collapse of ecosystems, making them more vulnerable to disturbances such as climate change, natural disasters, and human activities. For instance, the decline in bee populations affects pollination, which is crucial for crop production and food security.
Ecosystem services, which are benefits provided by natural environments, are vital to human economies. These include pollination, water purification, disease control, and climate regulation. According to the World Economic Forum, more than half of the world’s GDP is moderately or highly dependent on nature and its services. The loss of biodiversity could result in significant economic costs, affecting agriculture, fisheries, forestry, and tourism.
While climate change and biodiversity loss are interconnected, they present distinct challenges. Greenhouse gas emissions primarily drive climate change and can be addressed through mitigation strategies such as renewable energy and carbon sequestration. Biodiversity loss, however, is driven by a combination of factors including habitat destruction, pollution, overexploitation, invasive species, and climate change itself. The complexity of biodiversity loss requires a multifaceted approach. Unlike climate change, which can be measured in terms of temperature rise and carbon emissions, biodiversity involves a multitude of species and ecosystems, each with its unique interactions and dependencies.
Given the critical importance of biodiversity, it is essential to increase our focus and efforts on its conservation. Protecting existing natural habitats and restoring degraded ecosystems are vital steps. This involves creating and managing protected areas, reforestation, and habitat rehabilitation projects. Adopting sustainable agricultural, forestry, and fishing practices can help reduce the impact on biodiversity. This includes promoting agroecology, sustainable fisheries management, and reducing deforestation.
Why and How Technology Can Have a Positive Impact on Biodiversity
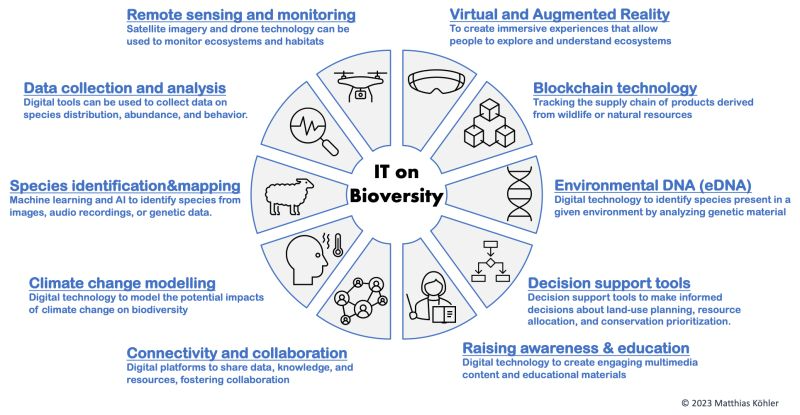
The intersection of technology and biodiversity conservation presents an unprecedented opportunity to address some of the most pressing environmental challenges of our time. Technology can significantly enhance our ability to monitor, understand, and protect ecosystems. Remote sensing and monitoring technologies, for example, allow us to observe vast and inaccessible areas of the planet, providing critical data that can inform conservation strategies and policy decisions. Drones and satellites offer real-time insights into deforestation, habitat destruction, and illegal activities, enabling swift action to mitigate these threats.
Moreover, advancements in data collection and analysis empower researchers with the tools to gather and process vast amounts of information on species distribution and ecosystem health. Citizen science platforms like iNaturalist democratize data collection, engaging the public in conservation efforts and generating large datasets that were previously unimaginable . This participatory approach not only enhances scientific research but also fosters a greater public understanding and appreciation of biodiversity.
Machine learning and AI are revolutionizing species identification and mapping, making it possible to process and analyze data with unprecedented accuracy and speed. These technologies help track population trends and identify critical habitats, guiding conservation efforts to where they are most needed. Predictive modeling tools further aid in understanding the impacts of climate change on biodiversity, allowing us to develop proactive conservation strategies and mitigate potential threats.
Blockchain technology introduces transparency and accountability in conservation finance and resource management. By ensuring that funds are used effectively and ethically, blockchain can enhance the credibility and impact of conservation projects. Additionally, eDNA analysis offers a non-invasive, cost-effective method for monitoring biodiversity, particularly in aquatic environments, making it a valuable tool for detecting and protecting rare and elusive species.
Virtual reality and augmented reality technologies provide immersive educational experiences, helping people connect with nature and understand the importance of conservation efforts. These technologies can inspire empathy and drive positive behavioral changes, crucial for the long-term success of biodiversity conservation.
The progress made in these areas over the past year demonstrates that technology can indeed be a force for good. By leveraging these innovative solutions, we can make significant strides in protecting and preserving the biodiversity of our planet. Technology not only enhances our capabilities but also fosters global collaboration and engagement, uniting individuals, organizations, and governments in the shared goal of conservation. As we continue to navigate the digital frontier, it is essential to harness the power of technology to create a sustainable and biodiverse future for all.
Here are some recent exciting startups and initiatives positively impacting biodiversity conservation through innovative technology.
1. Remote Sensing and Monitoring
- Planet Labs provides daily high-resolution images of Earth’s surface, helping detect deforestation and illegal activities. Their constant monitoring helps keep track of changes in land cover and vegetation.

- Wildlife Drones combines drones with radio-tracking technology to monitor wildlife effectively. This system is used to track animal movements and gather valuable data on habitat use and threats.

2. Data Collection and Analysis
- iNaturalist, a joint initiative by the California Academy of Sciences and the National Geographic Society, allows users to upload observations of biodiversity, creating a valuable database verified by experts.

- EarthRanger by Vulcan Inc. integrates various data sources (including GPS tracking, camera traps, and human reports) into a unified platform for wildlife conservation and protected area management.

3. Species Identification and Mapping
- BirdSAT utilizes AI and computer vision to classify and map bird species from both ground-level and satellite images, providing comprehensive data for monitoring bird populations and their habitats.
- Fieldin offers advanced sensors and a scouting app to manage pest control in agriculture, integrating data from various stages of pest management to ensure accurate species identification and effective intervention.

4. Climate Change Modeling
- Climate Engine leverages satellite and climate data for real-time environmental monitoring and forecasting. Their tools model the impacts of climate change on ecosystems, helping identify vulnerable species.

- Conservation International’s Moore Center for Science uses predictive modeling to assess climate impacts on biodiversity and aid in developing targeted conservation strategies.

5. Connectivity and Collaboration
- Global Biodiversity Information Facility (GBIF) is an international network providing open access to biodiversity data, facilitating data sharing among researchers and conservationists worldwide.

- Group on Earth Observations Biodiversity Observation Network (GEO BON) works to improve the acquisition, coordination, and delivery of biodiversity observations and related services to users, including decision-makers and the scientific community.

6. Raising Awareness and Education
- Beeodiversity uses bees as natural bioindicators to monitor environmental health. By analyzing pollen collected by bees, they provide data on plant biodiversity, pollutants, and pesticides, raising awareness among businesses and authorities.

- Virry VR offers immersive wildlife experiences that educate and engage the public, fostering empathy and understanding of conservation challenges through virtual reality.

7. Decision Support Tools
- ClimateView provides a platform that combines scientific modeling and machine learning to help cities understand and act on climate challenges. Their tools assist in decision-making processes related to urban planning and biodiversity conservation.

- Insight Robotics uses advanced data analytics to help manage and protect natural assets by monitoring environmental risks, including forest health and biodiversity. Their technology supports decision-makers in prioritizing conservation efforts.

8. Environmental DNA (eDNA)
- eDNA analysis uses digital technology to identify species present in an environment by analyzing their genetic material found in soil, water, or air samples. This helps researchers monitor biodiversity in a non-invasive and cost-effective manner.
- Dartmouth Ocean Technologies (DOT) develops autonomous eDNA samplers that detect biological genomic signatures underwater. This technology helps marine biologists monitor marine biodiversity non-invasively and cost-effectively.

- Nucleic Sensing Systems (NS2) provides real-time monitoring of species through their eDNA trackers, which offer genetic abundance data autonomously, useful for detecting rare or elusive species.

9. Blockchain Technology
- InvestConservation tokenizes high-value conservation projects, allowing investors to own carbon and biodiversity credits. Blockchain ensures transparency and security in transactions, directly supporting forest conservation.

- ReSEA uses a utility token to fund ocean ecosystem restoration projects. Each transaction supports environmental organizations, aligning economic incentives with conservation goals through a deflationary currency system.

10. Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR)
- Virry VR provides immersive wildlife experiences, helping users understand and empathize with conservation challenges. This application raises awareness about biodiversity issues by allowing users to interact with animals in their natural habitats virtually.

- iNaturalist integrates AR to engage citizen scientists in biodiversity monitoring. Users can explore local species in augmented reality, contributing to species identification and data collection efforts.
